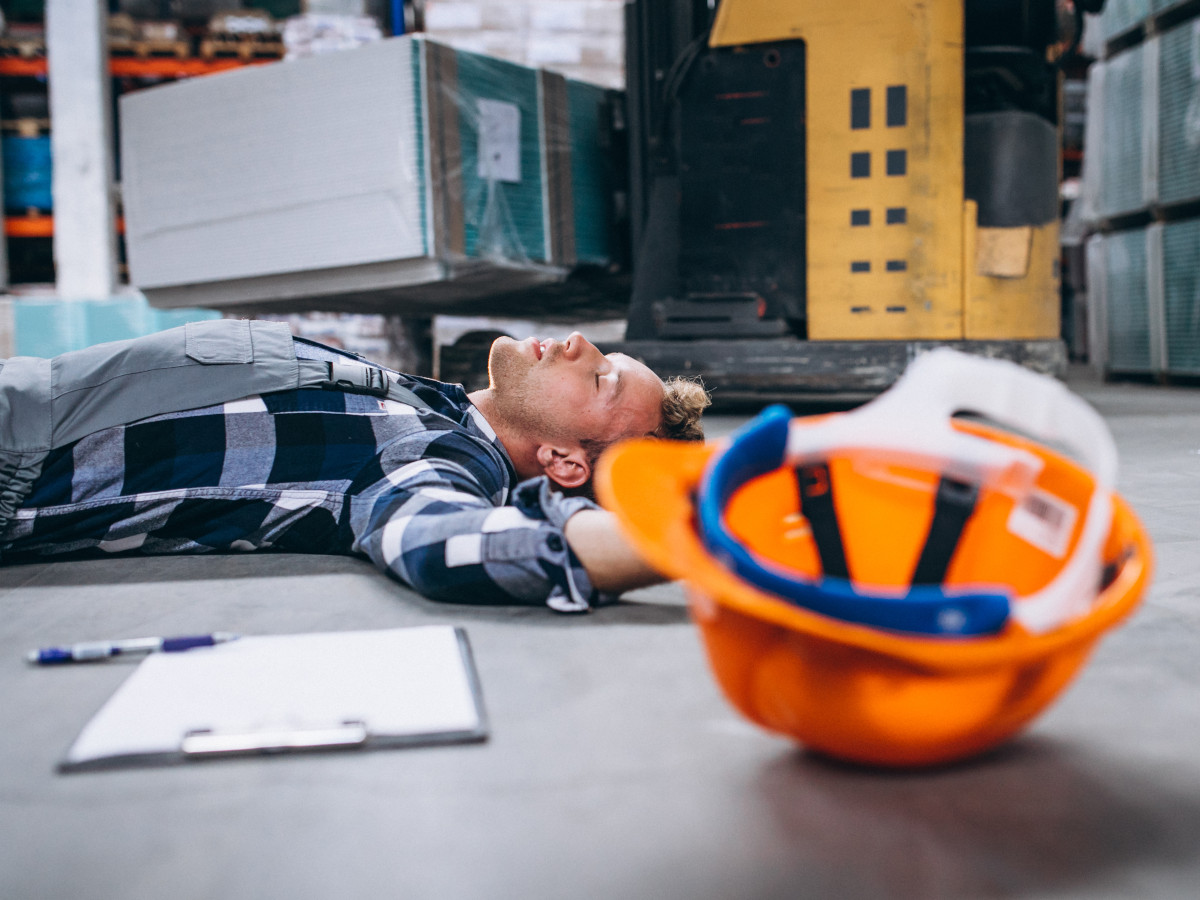
In the age of automation and robotization, many production lines are equipped with machines. They carry out the production process with high efficiency. Nevertheless, very often such machines cooperate with a human being. Unfortunately, this cooperation is sometimes dangerous and is subject to many restrictions. Still, in the case of high automation, this proves insufficient. The industry is yet to reach full worker safety. Can safety systems on production lines and warehouse halls be improved, and how?
Human and robot cooperation – impediments and obstructions
Cobotization, i.e. the cooperation of man and machine, is not fully safe yet. There are several procedures to support and ensure the safety of those working side by side with a robot. Even so, those procedures have their drawbacks. Additionally, the workers themselves, often wanting to speed up the production process, can “cheat” safety systems. Thus, they are creating an environment conducive to unfortunate accidents. What does this look like in practice?
Zones, distances, and fences
The current level of robotization and automation of work on production lines and in warehouses requires maintaining a safe distance from an operating robot. Hence, to ensure proper distance, designers and system integrators rely on the construction of fences. In this way, they designate a restricted zone. And while the robot is operating, the worker must be outside this zone.
Disadvantages of a solution based on physical barriers
From a practical point of view, such an application has four major disadvantages:
- barriers take up a considerable amount of space, which means that fewer machines can be placed in a given production area.
- physical safety curtains and partitions can be easily cheated.
- failure to meet the system’s safety conditions unnecessarily stops the machine’s operation, despite the absence of a worker in the restricted zone.
- only a handful of workers are authorized to deactivate the alarm of a violated safety zone. Consequently, the process of bringing a machine back into operation takes a long time. In addition, the workers have to stop doing their job in order to deactivate the alarm.
There are many documented cases of workers violating safety zone protection. As a result, mishaps have occurred. For example, a zone that requires a worker to close a safety gate can be fooled by sealing the lock with duct tape. This will cause the production line to operate despite the barrier’s gate being open. There are also times when an employee fails to close the gate. Hence, the machine fails to do its job – it’s not running for safety reasons.
Alternatives to conventional safety systems: virtual safety curtains
What are virtual safety curtains and how they work
These are systems that, using algorithms and images from either cameras (one or more) or lasers or radio waves, are able to recognize whether a designated safety zone has been violated. The machine receives notification of this event and performs a defined action, such as stopping. In this way, the need to build physical safety barriers can be partially or completely eliminated. The way virtual safety curtains work is well illustrated in the video below.
Virtual safety curtains without human recognition system
Safety systems that allow for virtual safety curtains in a factory or warehouse are beginning to appear on the market. There are currently only two such solutions worldwide. Thanks to them it is possible to:
- save space of factory floors and warehouses;
- avoid curtain errors (an under-attached gate) and hacking.
While these are useful features, they may not be sufficient for highly automated factories. An example disadvantage of virtual safety curtain systems is that if a second robot or object appears in the zone, the safety action will be executed. This can be a problem when, for example, a robot cooperates with both human and self-driving AGV.
Virtual safety curtains with human recognition system
We are still at the dawn of the era of advanced safety systems. Demand from manufacturers of autonomous machines has accelerated the development of work on such systems, but most of them are not dedicated to factories. Therefore, in this category, Thermosafety is a pioneering product. It’s the only system distinguishing humans from the rest of the environment in a factory floor or warehouse. The use of virtual safety curtains combined with human recognition further allows for:
- reliable restricted zones safeguarding;
- execution of a programmed action when a human crosses the boundaries of the zone: slowing the robot down or stopping it completely;
- lack of reaction to new objects and machines that appear in the safety zone.
At this stage, our system improves the safety of existing restricted zones. We are working on making Thermosafety capable of completely replacing fences in factories. What’s more, we have begun the certification process. Once it is completed, our safety system will be able to completely replace physical safety barriers. If you want to be up to date with information about Thermosafety intelligent safety system, you can follow us on LinkedIn or sign up for our Newsletter.